Tanks serve as indispensable vessels across various industries, facilitating the storage and transportation of liquids and gases. Yet, the effectiveness of these tanks often hinges not only on their structural integrity but also on the accessories accompanying them. From ladders facilitating access to railings ensuring safety, each accessory plays a crucial role in optimizing tank functionality. In this article, we delve into the production and installation processes of these essential components, shedding light on their significance in the realm of industrial operations.
1. Ladders: Ascending Access with Safety in Mind
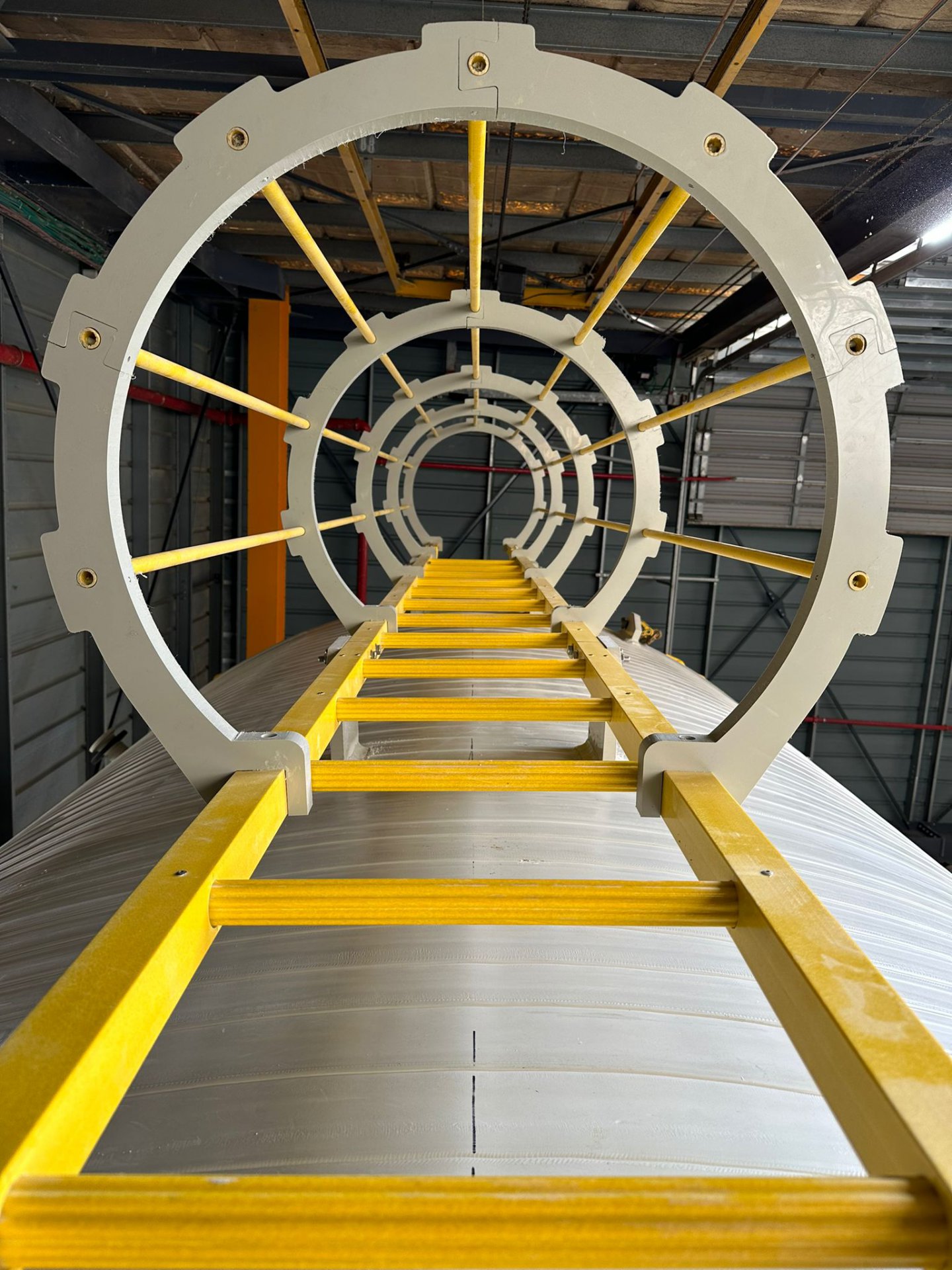
Ladders stand as the primary means for personnel to access tank roofs and other elevated components safely. Production begins with the selection of durable materials, typically FRP, ensuring resistance to corrosion and structural stability. Precision engineering ensures the fabrication of ladders meeting stringent safety standards, with anti-slip rungs and robust construction.
Installation of ladders demands meticulous planning, adhering to regulatory guidelines regarding height, spacing, and anchorage. Welding or bolting methods secure the ladder to the tank structure, with emphasis placed on load-bearing capacity and stability. Regular maintenance and inspection further guarantee the integrity of these vital access points, mitigating risks and enhancing operational efficiency.
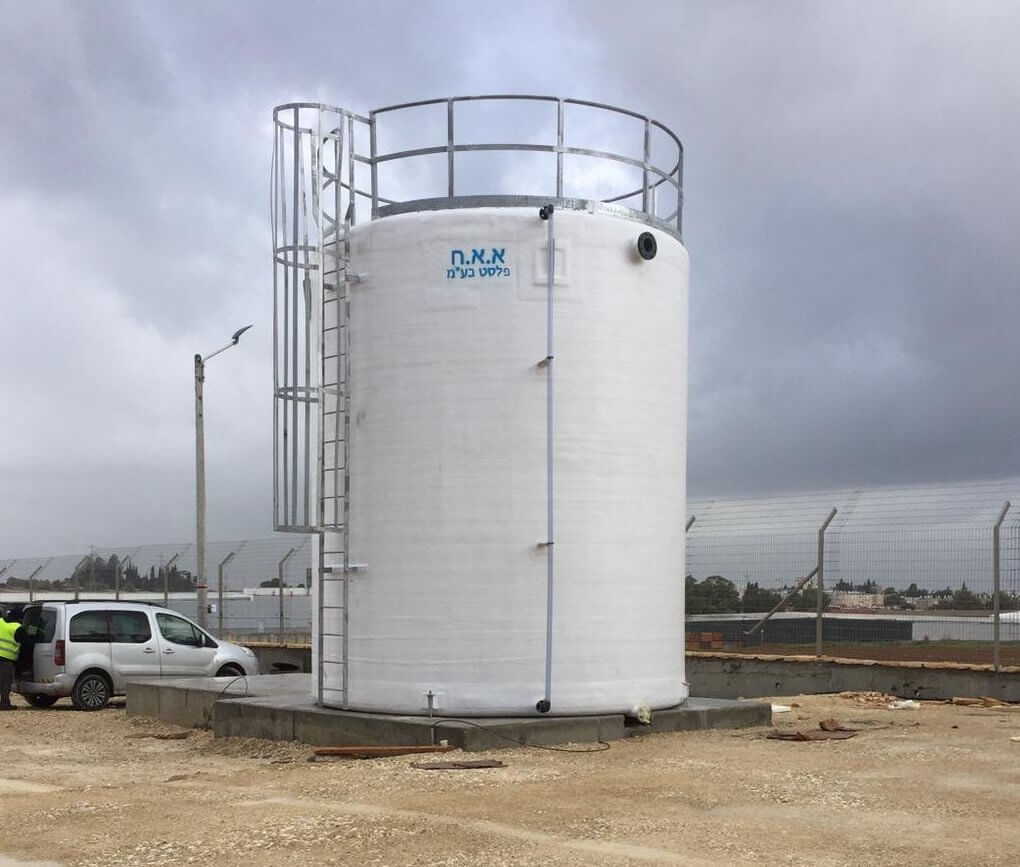
2. Railings: Safeguarding Personnel and Equipment
Railings encircling tank perimeters serve as crucial safety barriers, preventing accidental falls and providing support during maintenance activities. Fabrication involves the crafting of robust railing systems from materials such as steel or fiberglass, tailored to withstand harsh environmental conditions and ensure long-term durability.
Installation procedures prioritize structural stability, with welders employing precision techniques to affix railings securely to tank exteriors. Height and spacing adhere to safety regulations, with additional features such as toeboards and mid-rails enhancing protection. Regular inspections and maintenance routines uphold railing integrity, fostering a secure working environment conducive to productivity and employee well-being.
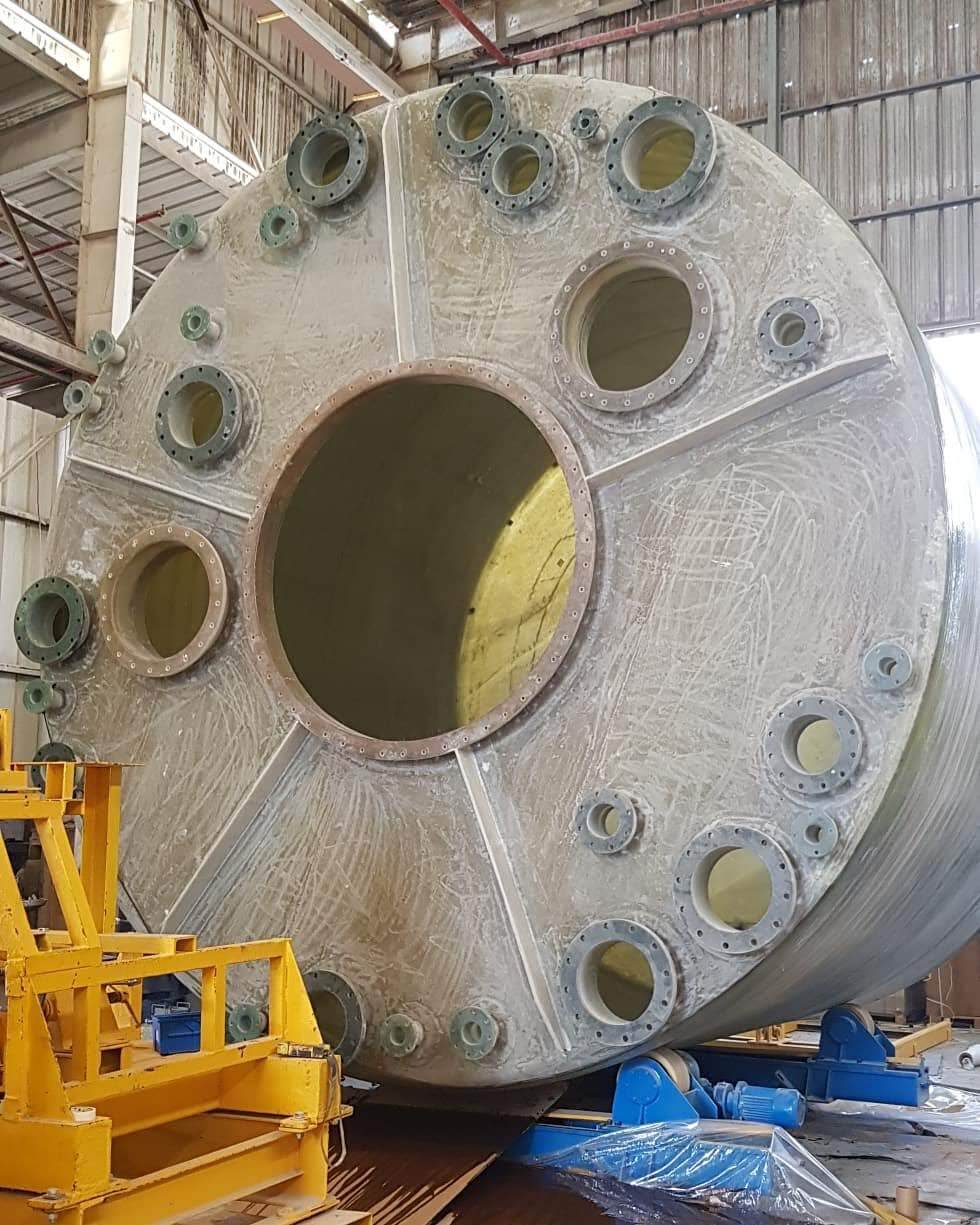
3. Manholes: Gateway to Maintenance and Inspection
Manholes represent access points crucial for routine maintenance, inspection, and cleaning operations within tanks. Manufactured from corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or carbon steel, these components undergo stringent quality control measures to ensure airtight seals and structural integrity.
Installation involves precision cutting and welding techniques, with emphasis placed on maintaining seal integrity and structural stability. Gaskets and locking mechanisms provide additional security, facilitating easy access while preventing leaks and contamination. Regular inspection and maintenance of manholes safeguard against corrosion and wear, ensuring uninterrupted operational performance.
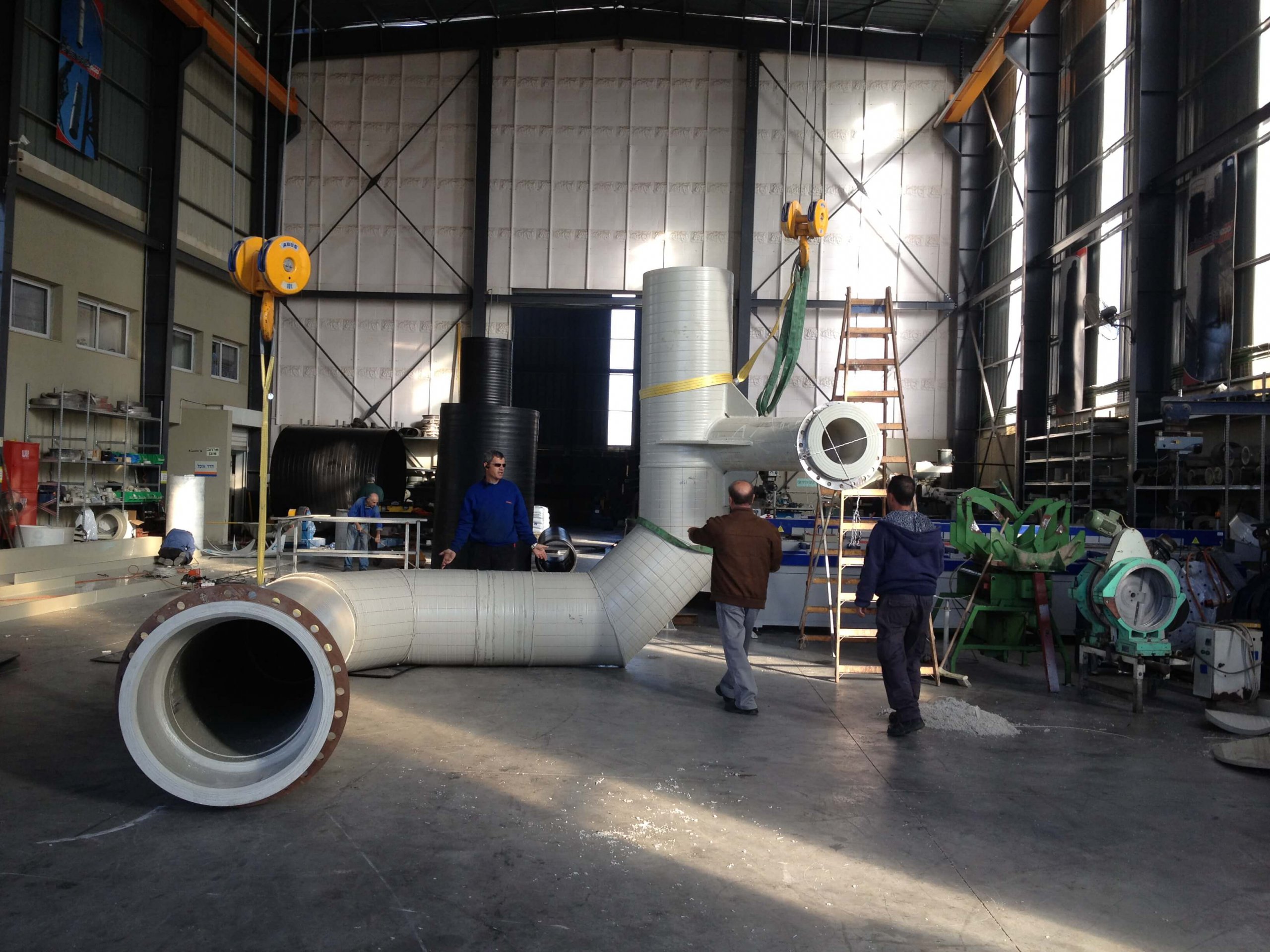
4. Ports and Connections: Seamless Integration with Piping Systems
Ports and connections serve as vital interfaces linking tanks with piping systems, facilitating fluid transfer and process control. Production entails the fabrication of robust port assemblies from materials compatible with stored substances, such as stainless steel or specialized alloys.
Installation procedures focus on precision alignment and sealing, minimizing the risk of leaks and ensuring seamless integration with existing piping networks. Flange connections or welded joints secure ports in place, with gaskets providing additional sealing protection. Regular inspection and maintenance routines safeguard against corrosion and degradation, preserving operational efficiency and fluid integrity.
In conclusion, the production and installation of tank accessories encompass a diverse array of components essential for optimizing functionality and ensuring operational safety. From ladders enabling access to railings safeguarding personnel, each accessory plays a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency and mitigating risks within industrial environments. By adhering to stringent fabrication standards and maintenance protocols, stakeholders can uphold the integrity of these vital components, thereby fostering a secure and productive operational landscape.